About LMD
Origin and Characteristics
In recent years, the government has been promoting a policy of "developing cultural and creative industries", which is a global force per se in the 21st century. Owing to this policy and contemporary trends, the Ministry of Education approved the university’s application to establish the "the Department of Learning and Materials Design” (hereafter DLMD). DLMD was formally established on 1 August 2011 by incorporating the existing Graduate Institute of Curriculum and Instruction, founded in 2000.
DLMD is one of the university’s most distinctive departments since it is a cultural and creative institution aimed at cultivating cultural and creative talents in the field of education, especially those in learning materials design. Teaching and learning materials used in schools are included in the term 'materials design', as well as everyday-life learning materials (including printing and multi-media) for children and adolescents. These students will become cross-disciplinary experts who are taught in the three fields - education, science and art - across which DLMD curriculum is distributed. The educational courses focus on the topics of curriculum and instruction (hereafter CI), as well as the necessary expertise for students in the cultural and creative design. In addition, the objectives of science courses place more attention on the applications of information technology, and the targets of art courses focus on the development of aesthetic design. In the other words, the CI courses equip students with primary contents to engage in the cultural and creative design, while the science and art courses equip students with main tools to engage in the cultural and creative design. In short, the foundation of DLMD is a crossing over of learning materials design and CI. The solid theoretical basis of CI associating with information technology and aesthetic design indicates the development orientation of DLMD.
Educational Objectives
Undergraduate Program
1. Developing the mastery of learning and materials design for innovators.
2. Nurturing intellectuals who are well-versed in information technology and possess aesthetic appreciation.
3. Cultivating cultural trendsetters who are sensitive to urban trends with humanistic solicitude.
Postgraduate Program
1. Cultivating outstanding researchers of CI to raise academic standards.
2. Nurturing curriculum leaders to improve school practice in the Taipei Metropolitan area.
3. Promoting and spreading new knowledge of CI for education innovation.
4. Participating in international exchanges of CI to promote mutual development.
Core Capabilities
Undergraduate Program
1. Educational knowledge and skills of CI.
2. Information technology and aesthetic design knowledge.
3. Multimedia and learning design performance capabilities.
4. Research skills of social trends and educational issues.
5. Ethical commitment to teamwork and humanism.
Postgraduate Program
1. To explore the theory and practice of curriculum.
2. To explore the theory and practice of instruction.
3. To understand research methods & strategies for CI.
4. To apply learning technology in CI.
5. To put into practice the ethics of humanistic solicitude.
Faculty
The department employs nine full-time professors who are experts in their respective fields and involved in the reform of the national curriculum. The department also employs a strong lineup of industry professionals as lecturers. Working together with cultural and creative agencies in the Taipei Metropolitan area, the department offers a summer internship program overseen by professors and adjunct professional experts jointly for diversity learning.
Curriculum Framework
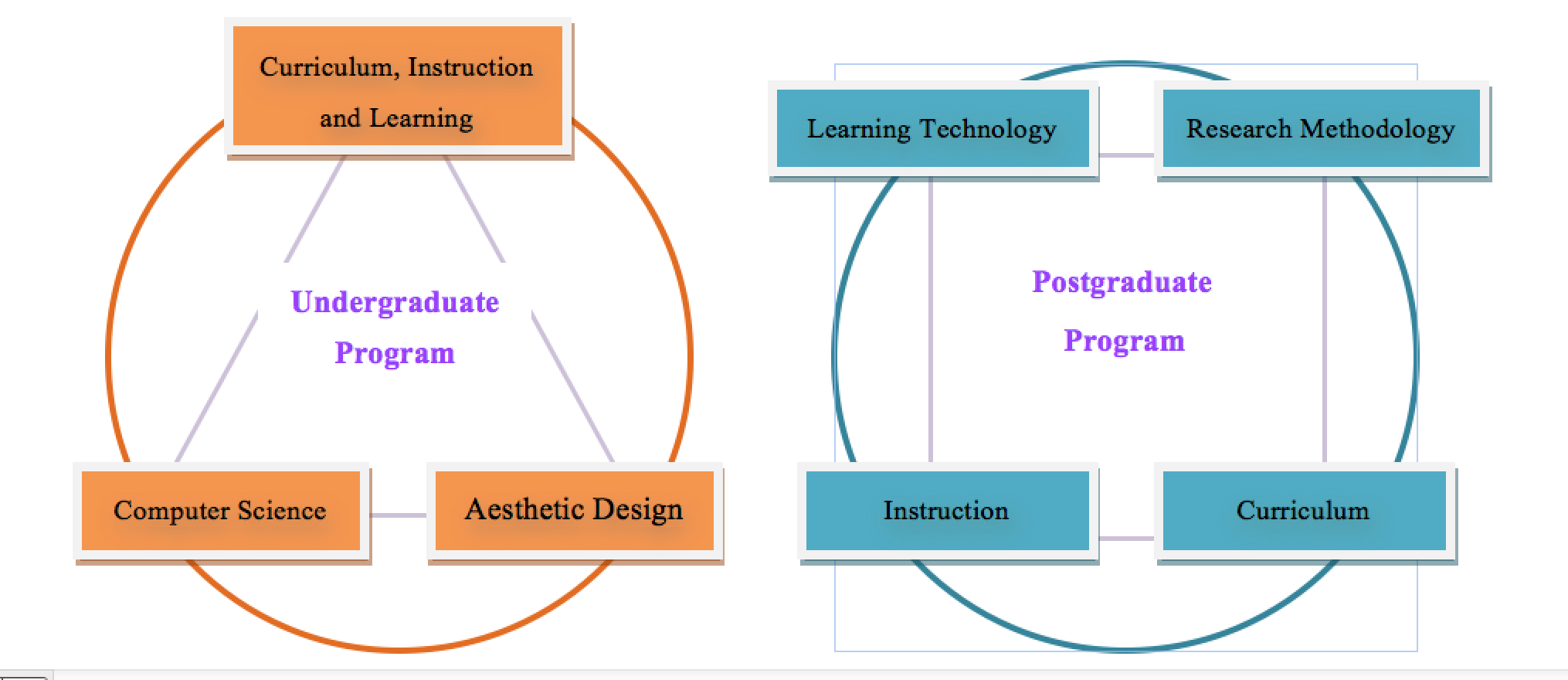
The course of study has three core areas: education, computer science, and aesthetic design. We expect to help students to develop a clear idea of "curriculum and instruction" (CI) and to form a good understanding of "society and culture", which will facilitate their practice in "graphic materials design" and "digital materials design".
Prospects
Undergraduate Program
1. Developing digital and traditional learning materials for use in schools.
2. Working in textbook-related industries.
3. Developing learning materials for children and adolescents.
4. Joining cultural and educational institutions or cultural and creative industries to design materials that promote education.
5. Obtaining continuing education in postgraduate programs at home or abroad.
Postgraduate Program
1. Serving as school principals or directors that participate in the Ministry/Department/Bureau of Education’s decision making and curriculum development process.
2. Serving as school community leaders that engage in curriculum development and innovation.
3. Doing research in CI research institutions and engaging in curriculum development and materials design.
4. Joining cultural and educational institutions or cultural and creative industries that design materials to promote education.
5. Obtaining continuing education in doctorate programs at home or abroad.
NUMBER OF STUDENTS
| Number of students | |
| The department | 157 |
| The graduate school | 130 |
| Total | 287 |
